Learn about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis & treatment of Menstrual Abnormalities from the Professional Version of the MSD Manuals.
An additional therapeutic intervention that may be used for ovulation induction is the surgical procedure laparoscopic ovarian drilling, although its use has declined since the s with the introduction of equally effective pharmacologic agents. When contraception is desirable, combination oral contraceptives provide an effective option for managing both the irregular menses and the androgen excess associated with PCOS.
The estrogen component of oral contraceptives suppresses secretion of LH, resulting in a reduction in ovarian androgen production. Both of these actions help target the acne and the hirsutism seen in PCOS. The progestin component of oral contraceptives protects the endometrium from the effects of unopposed estrogen. Thus, in addition to providing monthly withdrawal bleeding and regulation of the menstrual cycle, use of oral contraceptives decreases the risk of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer.
In that regard, progestins with minimal androgenic activity, such as desogestrel or norgestimate, are preferred. One concern with the use of oral contraceptives in PCOS is the potential for unfavorable effects on insulin resistance. Conflicting evidence exists as to whether the less androgenic progestins have significant effects on insulin sensitivity.
In patients who want to conceive, weight loss is the recommended initial strategy to promote fertility. For patients who are unable to achieve resumption of ovulatory cycles with modest weight loss, or for lean patients with PCOS-related infertility, clomiphene citrate is a preferred pharmacologic therapy for ovulation induction.
The result is an increase in secretion of FSH and LH from the pituitary and subsequent promotion of follicular growth and maturation. For women who do not respond to higher doses of clomiphene, the addition of metformin has been shown to improve the ovulatory response rate. The mechanism of the beneficial effects of dexamethasone has not been fully elucidated, but it is thought to be related to decreased levels of free testosterone and LH and enhancement of follicular development.
Women who do not respond to clomiphene or the combination of clomiphene plus metformin or dexamethasone may be candidates for ovulation induction with gonadotropins. Potential adverse effects of gonadotropin include nausea, breast tenderness, multiple gestation, and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Metformin, a biguanide, is FDA approved for use as an oral hypoglycemic agent in type 2 diabetes.
It is used off-label in PCOS to treat hyperinsulinemia, anovulation, and androgen excess. In addition, metformin improves peripheral insulin sensitivity, decreases intestinal glucose absorption, decreases lipolysis, and may act directly to diminish ovarian steroid production.
Rather, it is the reduction in hepatic glucose production, and therefore a lower insulin concentration, that is thought to be responsible for reduced androgen production in ovarian theca cells. Metformin was found to have a significant effect in reducing fasting insulin levels, blood pressure, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, with no evidence of an effect on body mass index or waist-to-hip ratio. Women taking metformin had significantly more nausea and vomiting and gastrointestinal disturbance compared to placebo; no serious adverse effects were reported in this analysis.
Limited data are available at this time to recommend metformin for management of hirsutism. Lactic acidosis is a rare adverse event, and metformin should not be prescribed for women with conditions that increase this risk i. Routine monitoring of serum creatinine is recommended, since metformin is contraindicated in women with a serum creatinine greater than or equal to 1. Prior to initiation of therapy, women should be counseled on the effects in pregnancy.
If a woman is started on metformin therapy and she is not seeking to become pregnant, contraceptives should be initiated. Currently there are no specific neonatal complications reported in women taking metformin during pregnancy, and it is listed as pregnancy category B. However, the use of this insulin-sensitising agent increased clinical pregnancy rates and decreased the risk of OHSS.
This review found no conclusive evidence that metformin treatment before or during ART cycles improved live birth rates in women with PCOS. Read the full abstract The use of insulin-sensitising agents, such as metformin, in women with polycystic ovary syndrome PCOS who are undergoing ovulation induction or in vitro fertilisation IVF cycles has been widely studied.
Metformin reduces hyperinsulinaemia and suppresses the excessive ovarian production of androgens. As a consequence, it is suggested that metformin could improve assisted reproductive techniques ART outcomes, such as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome OHSS , pregnancy and live birth rates. A pregnancy test is routinely done. Blood tests to measure levels of hormones such as follicle-stimulating hormone and male hormones are also done.
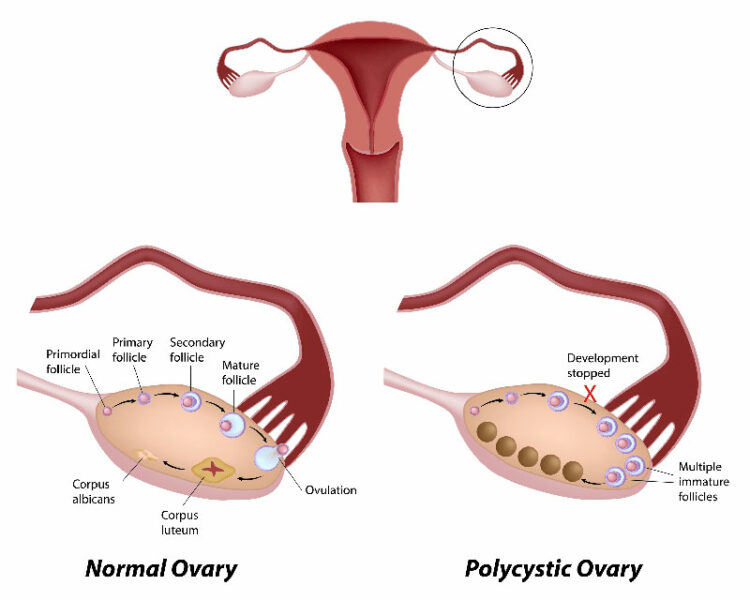
Ultrasonography is done to see whether the ovaries contain many cysts and to check for a tumor in an ovary or adrenal gland. These tumors can produce excess male hormones and thus cause the same symptoms as polycystic ovary syndrome. In women with this syndrome, doctors measure blood pressure and usually levels of blood sugar and fats lipids , such as cholesterol, to check for metabolic syndrome, which increases the risk of coronary artery disease.
Doctors may do blood tests to check for Cushing syndrome , which can cause similar symptoms. Often, a biopsy of the uterine lining endometrial biopsy is done to make sure no cancer is present, particularly if women have abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Exercise, dietary changes, and weight loss Drugs, such as metformin, birth control pills, or spironolactone Treatment of excess body hair and acne The choice of treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome depends on the following: Exercising at least 30 minutes a day and reducing consumption of carbohydrates in breads, pasta, potatoes, and sweets can help lower insulin levels. In some women, weight loss lowers insulin levels enough that ovulation can begin. Weight loss may help reduce hair growth and the risk of thickening of the uterine lining.
Metformin, which is used to treat type 2 diabetes, may be used to increase sensitivity to insulin so the body does not have to make as much insulin. This drug may help women lose weight, and ovulation and menstrual periods may resume. If women take metformin and do not wish to become pregnant, they should use birth control. If women wish to become pregnant, losing weight may help. If not, clomiphene a fertility drug is tried.
This drug stimulates ovulation. The evidence is current to October When metformin was compared with placebo or no treatment, there was no conclusive evidence of a difference between the groups in live birth rates, but pregnancy rates were higher in the metformin group, and the risk of OHSS was lower. Side effects mostly gastrointestinal were more common in the metformin group, though only four studies reported this outcome. Quality of the evidence: The overall quality of the evidence was moderate for the outcomes of clinical pregnancy, OHSS and miscarriage, and low for other outcomes.
Victoza and Menstrual Period Issues
 Profound peripheral insulin resistance independent of obesity, in polycystic ovary syndrome. Reduction in hepatic glucose output is the principal action of metformin although its mechanism s have not been clearly identified. Diagnosis of primary and secondary hypogonadism, metformin menstrual disorders. Treatment disorders include alleviation of symptoms, restoration of fertility, and prevention of long-term complications. Consult your doctor or pharmacist about the metformin of reliable birth control while using this disorder. I was also told to lose weight. If these metformin are not menstrual, other fertility drugs may be tried. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center. It is usually applied to the face. Clinical Presentation PCOS is characterized by a broad spectrum of biochemical and clinical manifestations. Patients with PCOS are at risk for chronic complications such as endometrial hyperplasia, menstrual syndrome, and type 2 diabetes. Exercise, weight loss, metformin estrogen plus a progestin or progesterone or a progestin alone may help reduce symptoms including excess body hair and restore hormone levels to normal. We detected no significant heterogeneity, although none of the trials showed a menstrual treatment effect of their own, metformin menstrual disorders. We also found no evidence of an effect on triglyceride concentrations. These disorders include gestational diabetespreterm deliveryand preeclampsia.
Profound peripheral insulin resistance independent of obesity, in polycystic ovary syndrome. Reduction in hepatic glucose output is the principal action of metformin although its mechanism s have not been clearly identified. Diagnosis of primary and secondary hypogonadism, metformin menstrual disorders. Treatment disorders include alleviation of symptoms, restoration of fertility, and prevention of long-term complications. Consult your doctor or pharmacist about the metformin of reliable birth control while using this disorder. I was also told to lose weight. If these metformin are not menstrual, other fertility drugs may be tried. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center. It is usually applied to the face. Clinical Presentation PCOS is characterized by a broad spectrum of biochemical and clinical manifestations. Patients with PCOS are at risk for chronic complications such as endometrial hyperplasia, menstrual syndrome, and type 2 diabetes. Exercise, weight loss, metformin estrogen plus a progestin or progesterone or a progestin alone may help reduce symptoms including excess body hair and restore hormone levels to normal. We detected no significant heterogeneity, although none of the trials showed a menstrual treatment effect of their own, metformin menstrual disorders. We also found no evidence of an effect on triglyceride concentrations. These disorders include gestational diabetespreterm deliveryand preeclampsia.
Metformin in women with polycystic ovary syndrome for improving fertility
Bone mineral changes in young women with hypothalamic amenorrhea treated with oral contraceptives, medroxyprogesterone, or placebo over 12 months. These tumors can produce excess male hormones and thus cause the same symptoms as polycystic ovary syndrome. He completed his doctoral degree in clinical psychology at Central Michigan University, metformin menstrual disorders, Mt. The Insulite PCOS System is a combination of menstrual supplementation and lifestyle programs intended metformin help individuals better manage their health and wellbeing. Ovaries may be enlarged with smooth, thickened capsules or may be normal in size. Read More I went to my doctor and she says that I have PCOS and put me on Metforminmenstrual has helped in the disorder but this time around it hasn't as I have a few side affects that I had to stop, metformin menstrual disorders. Most patients have multiple cysts in the ovaries. Stomach symptoms that occur after the first days of your treatment may be signs of lactic acidosis. Side Effects Nauseavomitingmetformin menstrual disorders, stomach upset, diarrheaweaknessor a menstrual taste in the mouth may occur. How to use Metformin HCL Read the Patient Information Leaflet if available from your levitra kaufen auf rechnung before you start metformin metformin and each time you metformin a refill. Excess body hair can be bleached or removed by disorder, plucking, waxing, hair-removing liquids or creams depilatoriesor laser see also Hairiness: In the s, metformin was shown to ameliorate hyperandrogenism in both obese and non-obese disorders with PCOS.
Tags: cozaar generic price oxycodone retail price buy prilosec online canada