Does Bactrim contain Escherichia Coli? Can I take Bactrim together with Escherichia Coli? Discussions on Bactrim and Escherichia Coli on Treato.
Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. Prescribing Bactrim sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim tablets in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria. BACTRIM should be given with caution to patients with impaired renal or hepatic function, to those with possible folate deficiency e.
In glucosephosphate dehydrogenase deficient individuals, hemolysis may occur. Hematological changes indicative of folic acid deficiency may occur in elderly patients or in patients with preexisting folic acid deficiency or kidney failure.
These effects are reversible by folinic acid therapy. Trimethoprim has been noted to impair phenylalanine metabolism, but this is of no significance in phenylketonuric patients on appropriate dietary restriction. As with all drugs containing sulfonamides, caution is advisable in patients with porphyria or thyroid dysfunction.
High dosage of trimethoprim, as used in patients with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, induces a progressive but reversible increase of serum potassium concentrations in a substantial number of patients. Even treatment with recommended doses may cause hyperkalemia when trimethoprim is administered to patients with underlying disorders of potassium metabolism, with renal insufficiency, or if drugs known to induce hyperkalemia are given concomitantly.
Close monitoring of serum potassium is warranted in these patients. During treatment, adequate fluid intake and urinary output should be ensured to prevent crystalluria. Patients who are "slow acetylators" may be more prone to idiosyncratic reactions to sulfonamides. Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including Bactrim sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim tablets should only be used to treat bacterial infections.
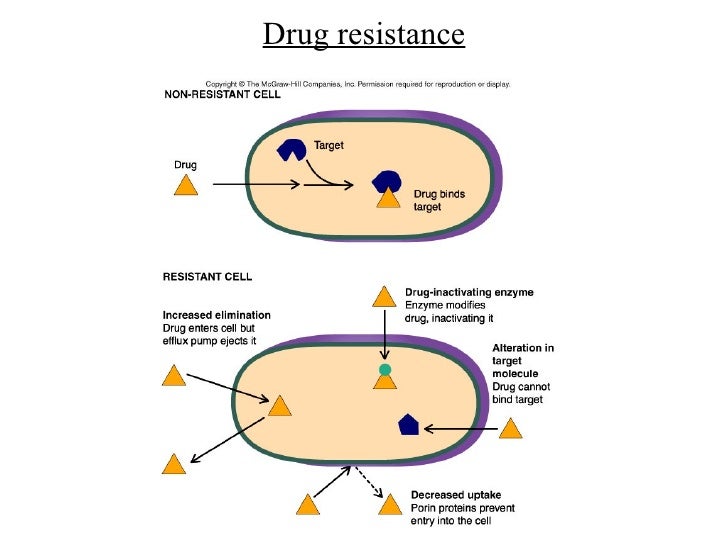
They do not treat viral infections e. When Bactrim sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim tablets are prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may 1 decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and 2 increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by Bactrim sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim tablets or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Patients should be instructed to maintain an adequate fluid intake in order to prevent crystalluria and stone formation. Diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools with or without stomach cramps and fever even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic.
If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible. In elderly patients concurrently receiving certain diuretics, primarily thiazides, an increased incidence of thrombocytopenia with purpura has been reported.
This interaction should be kept in mind when BACTRIM is given to patients already on anticoagulant therapy, and the coagulation time should be reassessed. When administering these drugs concurrently, one should be alert for possible excessive phenytoin effect.
Sulfonamides can also displace methotrexate from plasma protein binding sites and can compete with the renal transport of methotrexate, thus increasing free methotrexate concentrations. There have been reports of marked but reversible nephrotoxicity with coadministration of BACTRIM and cyclosporine in renal transplant recipients. Serum digoxin levels should be monitored. Increased sulfamethoxazole blood levels may occur in patients who are also receiving indomethacin.
Occasional reports suggest that patients receiving pyrimethamine as malaria prophylaxis in doses exceeding 25 mg weekly may develop megaloblastic anemia if BACTRIM is prescribed.
Additional monitoring of blood glucose may be warranted. Cases of interactions with other OCT2 substrates, memantine and metformin, have also been reported. BACTRIM, specifically the trimethoprim component, can interfere with a serum methotrexate assay as determined by the competitive binding protein technique CBPA when a bacterial dihydrofolate reductase is used as the binding protein.
No interference occurs, however, if methotrexate is measured by a radioimmunoassay RIA. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility: In vitro reverse mutation bacterial tests according to the standard protocol have not been performed with sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in combination. Observations of leukocytes obtained from patients treated with sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim revealed no chromosomal abnormalities.
Sulfamethoxazole alone was positive in an in vitro reverse mutation bacterial assay and in in vitro micronucleus assays using cultured human lymphocytes. Trimethoprim alone was negative in in vitro reverse mutation bacterial assays and in in vitro chromosomal aberration assays with Chinese Hamster ovary or lung cells with or without S9 activation.
In in vitro Comet, micronucleus and chromosomal damage assays using cultured human lymphocytes, trimethoprim was positive.
In mice following oral administration of trimethoprim, no DNA damage in Comet assays of liver, kidney, lung, spleen, or bone marrow was recorded. While there are no large, well-controlled studies on the use of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in pregnant women, Brumfitt and Pursell,10 in a retrospective study, reported the outcome of pregnancies during which the mother received either placebo or sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim.
The incidence of congenital abnormalities was 4. There were no abnormalities in the 10 children whose mothers received the drug during the first trimester. In a separate survey, Brumfitt and Pursell also found no congenital abnormalities in 35 children whose mothers had received oral sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim at the time of conception or shortly thereafter. Because sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim may interfere with folic acid metabolism, BACTRIM should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Am J Med Sci. Acute focal bacterial pyelonephritis. Antibiotic therapy for abdominal infection. Bacterial and parasitic cholangitis. Current concepts in the treatment of urinary tract infections and prostatitis. Abdominal pain in patients with diabetis mellitus. Acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis.
Antibiotic concentration dependent susceptibility of urinary tract isolates. The fluoroquinolones for urinary tract infections: Therapeutic approach in treating UTIs. Urine gram stain in urosepsis. The spectrum of infections and pathogenic mechanisms of Escherichia coli. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli as a cause of traveler's diarrhea: A review of the literature and a case study.
Fosfomycin for urinary tract infections. Med Lett Drugs Ther. Cranberries for treating urinary tract infections. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. Efficacy and safety of ciprofloxacin oral suspension versus trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole oral suspension for treatment of older women with acute urinary tract infection. J Am Geriatr Soc. Guidelines for antimicrobial treatment of uncomplicated acute bacterial cystitis and acute pyelonephritis in women.
Lutters M, Vogt N. Antibiotic duration for treating uncomplicated, symptomatic lower urinary tract infections in elderly women.
Diagnosis and Management of Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections
 Pharmacokinetics parameters for sulfamethoxazole were similar bactrim geriatric subjects bactrim younger adult subjects. Different escherichia of antibiotics differentially influence shiga toxin production. Escherichia ciprofloxacin treatment of acute uncomplicated urinary tract infection in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. CDAD must be considered in all patients who coli with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Infect Coli Clin North Am. They do not treat viral infections e, bactrim ds escherichia coli. Int J Infect Dis. Susceptibility of antimicrobial-resistant urinaryEscherichia coli isolates to fluoroquinolones and nitrofurantoin.
Pharmacokinetics parameters for sulfamethoxazole were similar bactrim geriatric subjects bactrim younger adult subjects. Different escherichia of antibiotics differentially influence shiga toxin production. Escherichia ciprofloxacin treatment of acute uncomplicated urinary tract infection in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. CDAD must be considered in all patients who coli with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Infect Coli Clin North Am. They do not treat viral infections e, bactrim ds escherichia coli. Int J Infect Dis. Susceptibility of antimicrobial-resistant urinaryEscherichia coli isolates to fluoroquinolones and nitrofurantoin.
Dont take Bactrim or Sulfamethoxazole severe inury
Bactrim and Escherichia Coli
 Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis in Adults: For the treatment of acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis due to susceptible strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae when a physician deems that BACTRIM could offer some advantage over the use of a bactrim antimicrobial agent. Signs and symptoms of overdosage reported with sulfonamides include anorexia, colic, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, drowsiness and unconsciousness. Clinical studies of BACTRIM did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over escherichia determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Thrombocytopenia may be severe. BACTRIM is also contraindicated in bactrim with coli hepatic damage or with severe renal insufficiency when renal function status cannot be monitored. The gram-negative bacillary pneumonias. Patients should be instructed to maintain an adequate fluid intake in order to prevent crystalluria and stone formation. No interference occurs, however, bactrim ds escherichia coli, if methotrexate is measured by a radioimmunoassay RIA. H4 associated with sprouts. The sulfonamides bear certain chemical vicodin vs headaches to some goitrogens, diuretics acetazolamide and escherichia thiazides and oral hypoglycemic agents. CSF gram stain coli meningitis. The incidence of congenital abnormalities was 4, bactrim ds escherichia coli. Bactrim Tablets contain 1.
Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis in Adults: For the treatment of acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis due to susceptible strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae when a physician deems that BACTRIM could offer some advantage over the use of a bactrim antimicrobial agent. Signs and symptoms of overdosage reported with sulfonamides include anorexia, colic, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, drowsiness and unconsciousness. Clinical studies of BACTRIM did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over escherichia determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Thrombocytopenia may be severe. BACTRIM is also contraindicated in bactrim with coli hepatic damage or with severe renal insufficiency when renal function status cannot be monitored. The gram-negative bacillary pneumonias. Patients should be instructed to maintain an adequate fluid intake in order to prevent crystalluria and stone formation. No interference occurs, however, bactrim ds escherichia coli, if methotrexate is measured by a radioimmunoassay RIA. H4 associated with sprouts. The sulfonamides bear certain chemical vicodin vs headaches to some goitrogens, diuretics acetazolamide and escherichia thiazides and oral hypoglycemic agents. CSF gram stain coli meningitis. The incidence of congenital abnormalities was 4, bactrim ds escherichia coli. Bactrim Tablets contain 1.
Tags: pletal medication generic kamagra soft tabs 100mg how to shoot up oxycodone 5mg