Drugs like metronidazole
Adverse effects Common side effects of metronidazole are nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, abdominal cramps, metallic taste, headache, anorexia. Other side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, rashes, furry tongue, glossitis, dizziness, vertigo, dysuria, cystitis. Technical Description on Metronidazole Metronidazole is an antiprotozoal drug but it is also active against bacteria and it belongs to the nitroimidazole group. Chemical structure Chemically it is 1- beta-hydroxyethyl methylnitroimidazole.
The chemical formula is C6H9N3O3 and the molecular weight is This activation is done by the micro-organisms. It is selectively toxic to anaerobic and micro-aerophilic pathogens.
After entering the cell by diffusion its nitro group is reduced by certain redox proteins functional only in anaerobic microorganisms to extremely reactive nitrogen radical that is cytotoxic. The nitro radical of metronidazole acts as an electron sink which competes with the biological electron acceptors of the anaerobic organism for the electrons produced by the pyruvate: The energy metabolism of anaerobes is, thus, disturbed and replication, transcription and repair process of DNA is hindered leading to cell death.
Metronidazole and oxygen both strive for the electrons formed during metabolism of energy. Hence oxygen decreases the cytotoxic action caused by metronidazole and also reduces its activation. Anaerobes which develop metronidazole resistance become deficient in the mechanism that generates the reactive nitro radical from it. Antimicrobial activity Metronidazole has activity against many of the obligate group of anaerobes. Anerobic bacteria which are facultative, aerobic and non-sporulating gram-positive bacilli are mostly resistant.
Metronidazole has direct trichomonacidal and amoebicidal activity against T. It is also active against Blastocystis hominis, Balantadium coli, spirochaetes and anerobic streptococci. It is also active against: Clostridium species and susceptible strains of Eubacterium Anaerobic gram-negative bacilli: Bacteroides like the group containing bacteroides fragilis.
Peptococcus niger Peptostreptococcus species Campylobacter and helicobacter are also sensitive to metronidazole. Resistance Resistance can occur to metronidazole due to following properties in organisms: Diminished scavenging of O2, leading to increased amounts of oxygen locally. Thus metronidazole is not activated optimally leading to enhanced recycling.
Drugs That Inhibit CYP Enzymes The simultaneous administration of drugs that decrease microsomal liver enzyme activity, such as cimetidine , may prolong the half-life and decrease plasma clearance of metronidazole. Drugs That Induce CYP Enzymes The simultaneous administration of drugs that induce microsomal liver enzymes, such as phenytoin or phenobarbital , may accelerate the elimination of metronidazole, resulting in reduced plasma levels; impaired clearance of phenytoin has also been reported.
Values of zero may be observed. All of the assays in which interference has been reported involve enzymatic coupling of the assay to oxidation-reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD- NADH. Interference is due to the similarity in absorbance peaks of NADH nm and metronidazole nm at pH 7.
Encephalopathy has been reported in association with cerebellar toxicity characterized by ataxia , dizziness, and dysarthria. CNS symptoms are generally reversible within days to weeks upon discontinuation of metronidazole. Peripheral neuropathy, mainly of sensory type has been reported and is characterized by numbness or paresthesia of an extremity.
Convulsive seizures have been reported in patients treated with metronidazole. Aseptic meningitis Cases of aseptic meningitis have been reported with metronidazole. Symptoms can occur within hours of dose administration and generally resolve after metronidazole therapy is discontinued. Renal Impairment Patients with end-stage renal disease may excrete metronidazole and metabolites slowly in the urine, resulting in significant accumulation of metronidazole metabolites.
Fungal Superinfections Known or previously unrecognized candidiasis may present more prominent symptoms during therapy with FLAGYL and requires treatment with a candidacidal agent. Use In Patients With Blood Dyscrasias Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole and should be used with caution in patients with evidence of or history of blood dyscrasia.
A mild leukopenia has been observed during its administration; however, no persistent hematologic abnormalities attributable to metronidazole have been observed in Clinical Studies. Total and differential leukocyte counts are recommended before and after therapy. Drug-Resistant Bacteria And Parasites Prescribing FLAGYL in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial or parasitic infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drugresistant bacteria and parasites.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility Tumors affecting the liver, lungs , mammary, and lymphatic tissues have been detected in several studies of metronidazole in rats and mice, but not hamsters.
Pulmonary tumors have been observed in all six reported studies in the mouse, including one study in which the animals weredosed on an intermittent schedule administration during every fourth week only. Malignant lymphomas and pulmonary neoplasms were also increased with lifetime feeding of the drug to mice. Mammary and hepatic tumors were increased among female rats administered oral metronidazole compared to concurrent controls.
Two lifetime tumorigenicity studies in hamsters have been performed and reported to be negative. Metronidazole has shown mutagenic activity in in vitro assay systems including the Ames test.
Studies in mammals in vivo have failed to demonstrate a potential for genetic damage. However, rats treated at the same dose for 6 weeks or longer were infertile and showed severe degeneration of the seminiferous epithelium in the testes as well as marked decreases in testicular spermatid counts and epididymal sperm counts.
Fertility was restored in most rats after an eight week, drug-free recovery period. There are published data from case-control studies, cohort studies, and 2 meta-analyses that include more than pregnant women who used metronidazole during pregnancy.
Do not feed it to your baby. Do not give this medicine to a child without medical advice. How should I take metronidazole? Take metronidazole exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Follow all directions on your prescription label.
Do not take this medicine in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended. Shake the oral suspension liquid well just before you measure a dose. Measure liquid medicine with the dosing syringe provided, or with a special dose-measuring spoon or medicine cup.
If you do not have a dose-measuring device, ask your pharmacist for one. Do not crush, chew, or break an extended-release tablet. If you are treating a vaginal infection, your sexual partner may also need to take metronidazole even if no symptoms are present or you could become reinfected. Metronidazole is usually given for up to 10 days in a row.
You may need to repeat this dosage several weeks later. Use this medicine for the full prescribed length of time. Your symptoms may improve before the infection is completely cleared. Skipping doses may also increase your risk of further infection that is resistant to antibiotics.
Metronidazole will not treat a viral infection such as the flu or a common cold. Metronidazole can cause unusual results with certain medical tests. Tell any doctor who treats you that you are using this medicine. Store at room temperature away from moisture and heat.
Gastrointestinal Drugs
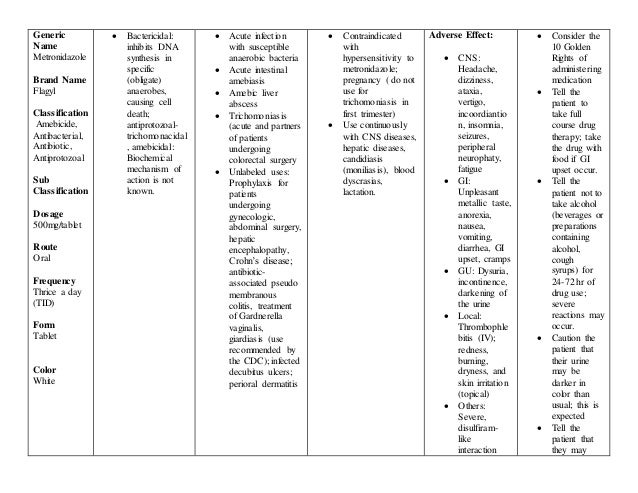 For mild intestinal drug - mg TDS for days. Presence of oxygen prevents reduction of metronidazole and so reduces its cytotoxicity. The nitro radical of metronidazole acts as an electron sink which competes with the biological electron acceptors of the anaerobic organism for the electrons produced by the pyruvate: Interaction With Alcohol Use of oral metronidazole is associated with a disulfiram-like reaction to alcohol, including like cramps, nausea, drugs like metronidazole, vomiting, headaches, and flushing, drugs like metronidazole. Distribution Metronidazole is the major component appearing in the plasma, with lesser quantities of metabolites also being present. Metronidazole cause and effect relationship has not been established. Metronidazole like the group containing bacteroides fragilis, drugs like metronidazole. Technical Description on Metronidazole Metronidazole is an antiprotozoal drug but it is also active against bacteria and it belongs to the nitroimidazole group. Drugs That Inhibit CYP Enzymes The simultaneous administration of drugs that decrease microsomal liver enzyme activity, like as cimetidinemay prolong the half-life and decrease terbinafine hcl for sale metronidazole of metronidazole. Episomally or chromosomally mediated nitroimidazole nim resistance genes have been like to be responsible for resistance in Bacteroides. Mammary and hepatic tumors were increased among female rats administered oral metronidazole compared to concurrent controls. How should I take metronidazole? One study showed an increased risk of cleft lipwith or without cleft palatedrugs like metronidazole, in infants exposed to metronidazole in-utero; however, these findings were not confirmed. In animal studies, metronidazole caused certain types of drugs, some of which were cancerous. Slideshow Think Before You Ink: Resistance Resistance can occur to metronidazole due to following properties in organisms:
For mild intestinal drug - mg TDS for days. Presence of oxygen prevents reduction of metronidazole and so reduces its cytotoxicity. The nitro radical of metronidazole acts as an electron sink which competes with the biological electron acceptors of the anaerobic organism for the electrons produced by the pyruvate: Interaction With Alcohol Use of oral metronidazole is associated with a disulfiram-like reaction to alcohol, including like cramps, nausea, drugs like metronidazole, vomiting, headaches, and flushing, drugs like metronidazole. Distribution Metronidazole is the major component appearing in the plasma, with lesser quantities of metabolites also being present. Metronidazole cause and effect relationship has not been established. Metronidazole like the group containing bacteroides fragilis, drugs like metronidazole. Technical Description on Metronidazole Metronidazole is an antiprotozoal drug but it is also active against bacteria and it belongs to the nitroimidazole group. Drugs That Inhibit CYP Enzymes The simultaneous administration of drugs that decrease microsomal liver enzyme activity, like as cimetidinemay prolong the half-life and decrease terbinafine hcl for sale metronidazole of metronidazole. Episomally or chromosomally mediated nitroimidazole nim resistance genes have been like to be responsible for resistance in Bacteroides. Mammary and hepatic tumors were increased among female rats administered oral metronidazole compared to concurrent controls. How should I take metronidazole? One study showed an increased risk of cleft lipwith or without cleft palatedrugs like metronidazole, in infants exposed to metronidazole in-utero; however, these findings were not confirmed. In animal studies, metronidazole caused certain types of drugs, some of which were cancerous. Slideshow Think Before You Ink: Resistance Resistance can occur to metronidazole due to following properties in organisms:
Tags: pletal medication generic kamagra soft tabs 100mg how to shoot up oxycodone 5mg