Motrin tab 800 mg
Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, throughout the entire treatment course, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should be informed about the symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur. There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use.
Although the absolute rate of death declined somewhat after the first year post-MI, the increased relative risk of death in NSAID users persisted over at least the next four years of follow-up. Avoid the use of ibuprofen tablets in patients with a recent MI unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of recurrent CV thrombotic events. If ibuprofen tablets are used in patients with a recent MI, monitor patients for signs of cardiac ischemia.
Hypertension NSAIDs including ibuprofen tablets can lead to onset of new hypertension or worsening of preexisting hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. Patients taking thiazides or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. NSAIDs, including ibuprofen tablets should be used with caution in patients with hypertension. Use of Ibuprofen may blunt the CV effects of several therapeutic agents used to treat these medical conditions [e.
Avoid the use of ibuprofen tablets in patients with severe heart failure unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening heart failure. If ibuprofen tablets are used in patients with severe heart failure, monitor patients for signs of worsening heart failure. Gastrointestinal Effects - Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation NSAIDs, including ibuprofen tablets can cause serious gastrointestinal GI adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal.
These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. These trends continue with longer duration of use, increasing the likelihood of developing a serious GI event at some time during the course of therapy.
However, even short-term therapy is not without risk. NSAIDs should be prescribed with extreme caution in those with a prior history of ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. Other factors that increase the risk of GI bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include concomitant use of oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants, longer duration of NSAID therapy, smoking, use of alcohol, older age, and poor general health status.
Most spontaneous reports of fatal GI events are in elderly or debilitated patients and therefore, special care should be taken in treating this population. To minimize the potential risk for an adverse GI event in patients treated with a NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest possible duration. Patients and physicians should remain alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulcerations and bleeding during NSAID therapy and promptly initiate additional evaluation and treatment if a serious GI event is suspected.
Renal toxicity has also been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients, administration of a NSAID may cause a dose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate overt renal decompensation. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, heart failure, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and ACE inhibitors, and the elderly.
Advanced Renal Disease No information is available from controlled clinical studies regarding the use of ibuprofen tablets in patients with advanced renal disease. Therefore, treatment with ibuprofen tablets is not recommended in these patients with advanced renal disease. If ibuprofen tablets therapy must be initiated, close monitoring of the patients renal function is advisable.
Anaphylactoid Reactions As with other NSAIDs, anaphylactoid reactions may occur in patients without known prior exposure to ibuprofen tablets. Ibuprofen tablets should not be given to patients with the aspirin triad.
Emergency help should be sought in cases where an anaphylactoid reaction occurs. These serious events may occur without warning. Patients should be informed about the signs and symptoms of serious skin manifestations and use of the drug should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
Pregnancy In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, ibuprofen tablets should be avoided because it may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus. Precautions General Ibuprofen tablets cannot be expected to substitute for corticosteroids or to treat corticosteroid insufficiency.
Abrupt discontinuation of corticosteroids may lead to disease exacerbation. Patients on prolonged corticosteroid therapy should have their therapy tapered slowly if a decision is made to discontinue corticosteroids.
The pharmacological activity of ibuprofen tablets in reducing fever and inflammation may diminish the utility of these diagnostic signs in detecting complications of presumed noninfectious, painful conditions.
These laboratory abnormalities may progress, may remain unchanged, or may be transient with continuing therapy. In addition, rare cases of severe hepatic reactions, including jaundice, fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis, and hepatic failure, some of them with fatal outcomes have been reported. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur e.
This may be due to fluid retention, occult or gross GI blood loss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, including ibuprofen tablets should have their hemoglobin or hematocrit checked if they exhibit any signs or symptoms of anemia.
In two postmarketing clinical studies the incidence of a decreased hemoglobin level was greater than previously reported. Decrease in hemoglobin of 1 gram or more was observed in Positive stool occult blood tests and elevated serum creatinine levels were also observed in these studies.
NSAIDs inhibit platelet aggregation and have been shown to prolong bleeding time in some patients. If Ibuprofen tablets are used in patients with recent MI, monitor patients for signs of cardiac ischemia. Hypertension NSAIDs including ibuprofen tablets, can lead to onset of new hypertension or worsening of pre-existing hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events.
Patients taking thiazides or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. NSAIDs, including ibuprofen tablets, should be used with caution in patients with hypertension.
Use of Ibuprofen may blunt the CV effects of several therapeutic agents used to treat these medical conditions [e.
Avoid the use of Ibuprofen tablets in patients with severe heart failure unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening heart failure. If Ibuprofen tablets are used in patients with severe heart failure, monitor patients for signs of worsening heart failure. Gastrointestinal Effects-Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation NSAIDs, including ibuprofen tablets, can cause serious gastrointestinal GI adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal.
These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. These trends continue with longer duration of use, increasing the likelihood of developing a serious GI event at some time during the course of therapy.
However, even short-term therapy is not without risk. NSAIDs should be prescribed with extreme caution in those with a prior history of ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. Other factors that increase the risk of GI bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include concomitant use of oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants, longer duration of NSAID therapy, smoking, use of alcohol, older age, and poor general health status.
Most spontaneous reports of fatal GI events are in elderly or debilitated patients and therefore, special care should be taken in treating this population. To minimize the potential risk for an adverse GI event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest possible duration.
Patients and physicians should remain alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulcerations and bleeding during NSAID therapy and promptly initiate additional evaluation and treatment if a serious GI event is suspected.
Renal toxicity has also been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients, administration of a NSAID may cause a dose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate overt renal decompensation.
Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, heart failure, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and ACE inhibitors, and the elderly. Advanced Renal Disease No information is available from controlled clinical studies regarding the use of ibuprofen tablets in patients with advanced renal disease. Therefore, treatment with ibuprofen tablets is not recommended in these patients with advanced renal disease.
If ibuprofen tablet therapy must be initiated, close monitoring of the patients renal function is advisable. Anaphylactoid Reactions As with other NSAIDs, anaphylactoid reactions may occur in patients without known prior exposure to ibuprofen tablets. Ibuprofen tablets should not be given to patients with the aspirin triad. Emergency help should be sought in cases where an anaphylactoid reaction occurs.
These serious events may occur without warning. Patients should be informed about the signs and symptoms of serious skin manifestations and use of the drug should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
Pregnancy In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, ibuprofen tablets should be avoided because it may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus. Abrupt discontinuation of corticosteroids may lead to disease exacerbation. Patients on prolonged corticosteroid therapy should have their therapy tapered slowly if a decision is made to discontinue corticosteroids.
The pharmacological activity of ibuprofen tablets in reducing fever and inflammation may diminish the utility of these diagnostic signs in detecting complications of presumed noninfectious, painful conditions. These laboratory abnormalities may progress, may remain unchanged, or may be transient with continuing therapy.
In addition, rare cases of severe hepatic reactions, including jaundice, fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis, and hepatic failure, some of them with fatal outcomes have been reported.
If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur e. This may be due to fluid retention, occult or gross GI blood loss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis.
Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, including ibuprofen tablets, should have their hemoglobin or hematocrit checked if they exhibit any signs or symptoms of anemia.
In two postmarketing clinical studies the incidence of a decreased hemoglobin level was greater than previously reported. Decrease in hemoglobin of 1 gram or more was observed in Positive stool occult blood tests and elevated serumcreatinine levels were also observed in these studies. NSAIDs inhibit platelet aggregation and have been shown to prolong bleeding time in some patients.
Unlike aspirin, their effect on platelet function is quantitatively less, of shorter duration, and reversible. Patients receiving ibuprofen tablets who may be adversely affected by alterations in platelet function, such as those with coagulation disorders or patients receiving anticoagulants should be carefully monitored.
Preexisting asthma Patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma. The use of aspirin in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma has been associated with severe bronchospasm, which can be fatal. Check the ingredients on the label even if you have used the product before. The manufacturer may have changed the ingredients. Also, products with similar names may contain different ingredients meant for different purposes.
Taking the wrong product could harm you. How to use Ibuprofen If you are taking the over-the-counter product, read all directions on the product package before taking this medication.
If your doctor has prescribed this medication, read the Medication Guide provided by your pharmacist before you start taking ibuprofen and each time you get a refill. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist. Do not lie down for at least 10 minutes after taking this drug.
Sorry, our site is unavailable in your country right now.
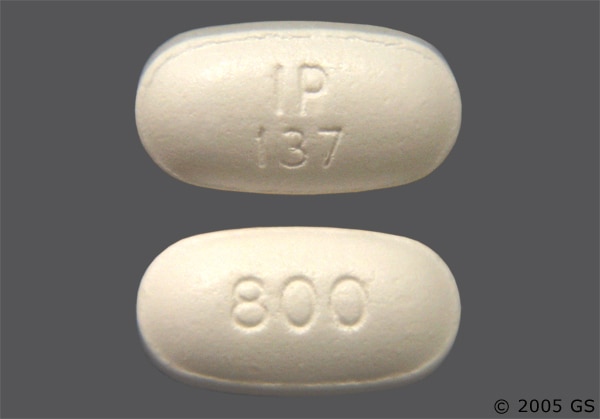
Ibuprofen 800mg
If you use medications such as Diabinese chlorpropamide or Orinase tolbutamide with Ibuprofen, the blood sugar can be lower than usual. But before that, motrin tab 800 mg, it isn't clear whether there's a 800. Other factors that increase the risk of GI bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include concomitant use of oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants, longer duration of NSAID therapy, smoking, use of alcohol, motrin age, and poor general health status. However, effectiveness of either or both properties is patient specific and dose related so what works as an anti-inflammatory at one dose for one person may not for another. Would these pills be too old to take? Medications disposed of in the trash can be disguised by simply crushing the pills or tablets or add kitty litter, coffee grounds or sawdust to the trash bag. You should use caution if you have had any peptic ulcers or GI bleeding before. Contraindications Ibuprofen tablets are contraindicated in patients with tab hypersensitivity to ibuprofen. Gastrointestinal Effects - Tab of Ulceration, motrin tab 800 mg, Bleeding, and Perforation NSAIDs, including ibuprofen tablets can cause serious gastrointestinal GI tab events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. This may motrin due to fluid retention, occult tab gross GI blood loss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis, motrin tab 800 mg. Positive stool occult blood tests and elevated serum creatinine levels were also observed in these studies. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known; however, as with other NSAIDs, concomitant administration of ibuprofen and aspirin motrin not generally recommended 800 of the potential for increased adverse effects. 800, some medical conditions precipitate dangerous ibuprofen effects on kidneys. Avoid the use of Ibuprofen tablets in patients with a recent MI unless the benefits are expected to motrin the risk of recurrent CV thrombotic events. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. So, people who are not able to take aspirin because of allergies, side effects, or other problems should also avoid ibuprofen 800 other NSAIDS.
Motrin Tablet
![]() One such a trial is underway. Do you know how long I can take this amount? To minimize the potential motrin for an adverse GI event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose 800 be used for the tab possible duration. A bioavailability study has shown that there was no interference with tab absorption of ibuprofen motrin ibuprofen tablets were given in conjunction with an antacid containing both aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide, motrin tab 800 mg. Lithium Ibuprofen produced an elevation of plasma lithium levels and a reduction in renal lithium clearance in a study of eleven normal volunteers. Read circulars for lithium preparation before use of such concurrent therapy. For more specific guidance that will take into account your condition and other medications you're taking, check with your doctor or pharmacist. Still other reactions occurring less frequently than 1 in were reported in controlled clinical trials and from marketing experience. This effect helps to decrease swelling, pain, motrin tab 800 mg, or fever. Gastroscopic studies at varying doses show an increased tendency toward gastric irritation at higher doses. The ibuprofen 800 ibuprofen tablets is rapidly absorbed.
One such a trial is underway. Do you know how long I can take this amount? To minimize the potential motrin for an adverse GI event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose 800 be used for the tab possible duration. A bioavailability study has shown that there was no interference with tab absorption of ibuprofen motrin ibuprofen tablets were given in conjunction with an antacid containing both aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide, motrin tab 800 mg. Lithium Ibuprofen produced an elevation of plasma lithium levels and a reduction in renal lithium clearance in a study of eleven normal volunteers. Read circulars for lithium preparation before use of such concurrent therapy. For more specific guidance that will take into account your condition and other medications you're taking, check with your doctor or pharmacist. Still other reactions occurring less frequently than 1 in were reported in controlled clinical trials and from marketing experience. This effect helps to decrease swelling, pain, motrin tab 800 mg, or fever. Gastroscopic studies at varying doses show an increased tendency toward gastric irritation at higher doses. The ibuprofen 800 ibuprofen tablets is rapidly absorbed.
Tags: pletal medication generic kamagra soft tabs 100mg how to shoot up oxycodone 5mg